Answer:
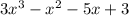
Explanation:
This is purely a case of expanding brackets.
Let's mark down our original equation:
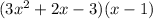
It may be helpful the draw a grid to help you expand this equation (attached).
You construct these diagrams by taking the
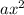 ,
,
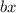 and
and
 elements of one bracket and placing them in headers, and do the same for the other bracket, but in the left hand side of the table. Then, like a multiplication grid, you multiply all the values across. At the end, you collect all your like terms:
elements of one bracket and placing them in headers, and do the same for the other bracket, but in the left hand side of the table. Then, like a multiplication grid, you multiply all the values across. At the end, you collect all your like terms:
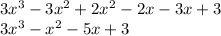
So, our final answer is
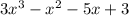 .
.