Answer:
Correct choice: b 4H
Step-by-step explanation:
Conservation of the mechanical energy
The mechanical energy is the sum of the gravitational potential energy GPE (U) and the kinetic energy KE (K):
E = U + K
The GPE is calculated as:
U = mgh
And the kinetic energy is:
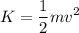
Where:
m = mass of the object
g = gravitational acceleration
h = height of the object
v = speed at which the object moves
When the snowball is dropped from a height H, it has zero speed and therefore zero kinetic energy, thus the mechanical energy is:
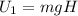
When the snowball reaches the ground, the height is zero and the GPE is also zero, thus the mechanical energy is:
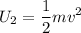
Since the energy is conserved, U1=U2
![\displaystyle mgH=(1)/(2)mv^2 \qquad\qquad [1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/jsa351d5x7m87s5s6ymvcgyzm5comarhnh.png)
For the speed to be double, we need to drop the snowball from a height H', and:
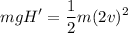
Operating:
![\displaystyle mgH'=4(1)/(2)m(v)^2 \qquad\qquad [2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/cdhtskgzxegf60na7ig3swt1i8c3vekt78.png)
Dividing [2] by [1]
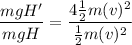
Simplifying:
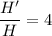
Thus:
H' = 4H
Correct choice: b 4H