Answer:
The mass of the piston must be 40.573 kilograms.
Step-by-step explanation:
From Fluid Mechanics, the absolute pressure is the sum of atmospheric pressure and manometric pressure. The manometric pressure is equivalent to the pressure done on the substance due to the weight of the piston:
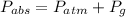 (1)
(1)
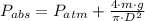 (2)
(2)
Where:
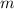 - Mass of the piston, measured in kilograms.
- Mass of the piston, measured in kilograms.
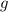 - Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
- Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
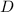 - Diameter of the piston, measured in meters.
- Diameter of the piston, measured in meters.
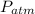 - Atmospheric pressure, measured in pascals.
- Atmospheric pressure, measured in pascals.
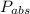 - Absolute pressure, measured in pascals.
- Absolute pressure, measured in pascals.
Now we clear the mass of the piston within the formula:
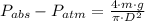
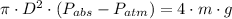
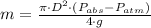
If we know that
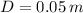 ,
,
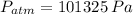 ,
,
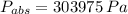 and
and
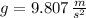 , then the mass of the piston must be:
, then the mass of the piston must be:
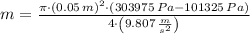
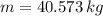
The mass of the piston must be 40.573 kilograms.