Answer:
The final velocity,
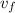 , is gd.
, is gd.
Step-by-step explanation:
The condition here is a free falling object. Thus from the third equation of motion under free fall, we have;
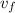 =
=
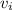 + 2gs
+ 2gs
where
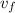 is the final velocity of the object,
is the final velocity of the object,
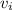 is the initial velocity of the object, g is the gravitational force and s is the height.
is the initial velocity of the object, g is the gravitational force and s is the height.
Since the object falls from a height of d, then
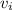 = 0 m/s, and s = d.
= 0 m/s, and s = d.
So that;
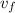 = 0 + 2gd
= 0 + 2gd
= 2gd
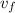 = 2gd
= 2gd
When the distance is
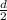 ,
,
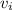 = 0 m/s.
= 0 m/s.
Then;
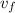 = 2g
= 2g
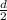
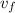 = g x d
= g x d
When the object falls through the height
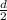 , then the final velocity is gd.
, then the final velocity is gd.