Answer: Black allele has frequency of 0.14.
Red allele has frequency of 0.86.
The frequency of heterozygotes is 0.241
Step-by-step explanation: Hardy-Weinberg model states the frequency of alleles in a population will stay in equilibrium as long as there are external influences. It is also used to determine alleles frequencies using the following equations:
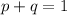
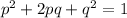
p represents frequency of dominant allele;
q represents frequency of recessive allele;
2pq is frequency of heterozygotes;
For the frequency of red allele, which is dominant, we can use:
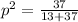
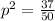
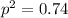
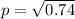
p = 0.86
For the black allele:
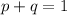
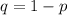
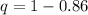
q = 0.14
Frequency of heterozygotes is
2pq = 2(0.86)(0.14)
2pq = 0.241
Frequencies for a population of Muscovy ducks are 0.86 for red allele, 0.14 for black allele and 0.241 for heterozygote.