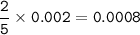Moles of potassium permanganate = 0.0008
Further explanation
Titration is a procedure for determining the concentration of a solution by reacting with another solution which is known to be concentrated (usually a standard solution). Determination of the endpoint/equivalence point of the reaction can use indicators according to the appropriate pH range
Reaction
5Na2C2O4(aq) + 2KMnO4(aq) + 8H2SO4(aq) ---> 2MnSO4(aq) + K2SO4(aq) + 5Na2SO4(aq) + 10CO2(g) + 8H2O(1)
The end point ⇒titrant and analyte moles equal
titrant : potassium permanganate-KMnO4
analyte : sodium oxalate - Na2C2O4
so moles of KMnO4 = moles of Na2C2O4
moles of Na2C2O4(mass = 0.2640 g, MW=134 g/mol) :
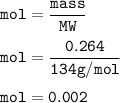
From equation, mol ratio Na2C2O4 : KMnO4 = 5 : 2, so mol KMnO4 :