Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
We are given the specific heat and change in temperature, so we should use this heat formula:
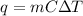
where m is the mass, C is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
We know the mass is 150 grams. The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g °C.
Let's find the change in temperature.
Subtract the initial temperature from the final temperature.
- ΔT= final temp - initial temp
- final= 95.0 °C and initial= 10.0 °C
- ΔT= 95.0 °C - 10.0 °C= 85.0 °C
Now we know all the values:
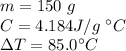
Substitute them into the formula.
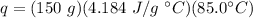
Multiply all three numbers together. Note that the grams (g) and degrees Celsius (°C) will cancel out. Joules (J) will be the only remaining unit.
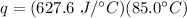
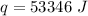
53,346 Joules of heat are required.