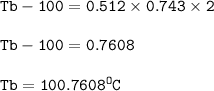The boiling point (in C) of a 0.743 m aqueous solution of KCI : 100.7608°C
Further explanation
Solutions from volatile substances have a higher boiling point and lower freezing points than the solvent
ΔTb = Tb solution - Tb solvent
ΔTb = boiling point elevation

For electrolyte solutions there is a van't Hoff factor = i
i = 1 + (n-1) α
n = number of ions from the electrolyte
α = degree of ionization, strong electrolyte α = 1, for non electrolytes i = 1
KCl⇒K⁺+Cl⁻⇒ electrolyte solution(2 ions K⁺ and Cl⁻), strong electrolyte α = 1
ΔTb=Kb.m.i
i = 1 + (n-1) α
i=1+(2-1).1=2
Kb for water (solvent) : 0.512 °C kg/mol
molal KCl = 0.743 m
The boiling point of solution :