Answer:
g = 0.85 m
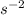
Step-by-step explanation:
g =
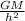
were; g is the acceleration due to Earth's gravity, G is Newton's gravitation constant (6.674 x
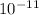 N
N
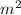
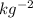 ), M is the mass of the earth (5.972 x
), M is the mass of the earth (5.972 x
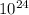 kg), and h is the distance of meteoroid to the earth.
kg), and h is the distance of meteoroid to the earth.
h = 3.40 x R
= 3.40 x 6371 km
h = 21661.4 km
= 21661400 m
Thus,
g =
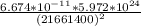
=
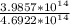
= 0.84944
g = 0.85 m
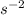
The acceleration due to the Earth's gravitation is 0.85 m
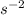 .
.