Answer:
V ≈ 2.9 L H₂
General Formulas and Concepts:
Chemistry - Atomic Structure
- Reading a Periodic Table
- Using Dimensional Analysis
Chemistry - Reactions
- Aqueous Solutions and states of matter
- Reaction Prediction
Chemistry - Gas Laws
Combined Gas Law: PV = nRT
- P is pressure
- V is volume in liters
- n is amount of moles of substance
- R is a constant - 62.4 (L · mmHg)/(mol · K)
- T is temperature in Kelvins
Temperature Conversion: K = °C + 273.15
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Define
Unbalanced RxN: Zn (s) + HCl (aq) → ZnCl₂ (aq) + H₂ (g)
Balanced RxN: Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl₂ (aq) + H₂ (g)
Given: 7.68 g Zn, 20.00 °C, 740 mmHg
Step 2: Identify Conversions
Kelvin Conversion
Molar Mass of Zn - 65.39 g/mol
Step 3: Convert
Stoichiometry:
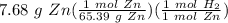 = 0.117449 mol H₂
= 0.117449 mol H₂
Temp Conversion: 20.00 + 273.15 = 293.15 K
Step 4: Find V
- Substitute: (740 mmHg)V = (0.117449 mol)(62.4 (L · mmHg)/(mol · K))(293.15 K)
- Multiply: (740 mmHg)V = 2148.45 L · mmHg
- Isolate V: V = 2.9033 L H₂
Step 5: Check
We are given 2 sig figs as our lowest. Follow sig fig rules and round.
2.9033 L H₂ ≈ 2.9 L H₂