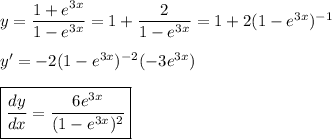9514 1404 393
Answer:
a) y' = x^2(3x·ln(6x) +1)
b) y' = 6e^(3x)/(1 -e^(3x))^2
Explanation:
The applicable rules for derivatives include ...
d(u^n)/dx = n·u^(n-1)·du/dx
d(uv)/dx = (du/dx)v +u(dv/dx)
d(e^u)/dx = e^u·du/dx
d(ln(u))/dx = 1/u·du/dx
__
(a)
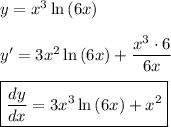
__
(b)