The force applied by the spring is calculated using Hooke's Law. Given a spring constant of 11 N/m and a displacement of 0.25 m, the spring applies a force of 2.75 N.
The force applied by a spring can be calculated using Hooke's Law, which is defined by the equation F = -kx, where F is the force exerted by the spring in newtons (N), k is the spring constant in newtons per meter (N/m), and x is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position in meters (m). In this case, the spring with a spring constant k of 11 N/m is stretched by 0.25 m. To find the force the spring applies, we multiply the spring constant by the displacement:
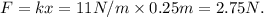
Therefore, the spring applies a force of 2.75 N when stretched by 0.25 m.