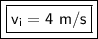
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
We are asked to find the cyclist's initial velocity. We are given the acceleration, final velocity, and time, so we will use the following kinematic equation.
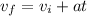
The cyclist is acceleration at 1.2 meters per second squared. After 10 seconds, the velocity is 16 meters per second.
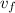 = 16 m/s
= 16 m/s - a= 1.2 m/s²
- t= 10 s
Substitute the values into the formula.
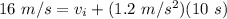
Multiply.
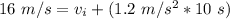
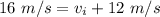
We are solving for the initial velocity, so we must isolate the variable
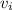 . Subtract 12 meters per second from both sides of the equation.
. Subtract 12 meters per second from both sides of the equation.
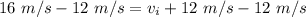
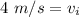
The cyclist's initial velocity is 4 meters per second.