Answer:
The volume will be 3.72 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
We can find the new volume by using the Ideal Gas Law:
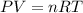
Where:
P: is the pressure
V: is the volume
n: is the number of moles
R: is the gas constant
T: is the temperature
Initially, we have:
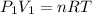 (1)
(1)
with V₁ = 6.2 L, P₁ = 201 kPa and nRT = constant
When the pressure is increased we have:
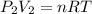 (2)
(2)
with V₂ =?, P₂ = 335 kPa and nRT = constant
By equating (1) and (2) we have:
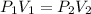
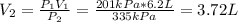
Therefore, the pressure is increased to 335 kPa the volume will be 3.72 L.
I hope it helps you!