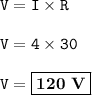The voltage needed = 120 V
Further explanation
Electric current (symbolized by the letter "i) is the amount of charge flowing in the conductor of each unit of time
Can be formulated:
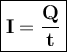
Q = charge (Coulomb)
t = time (seconds)
The international standard unit of electric current is Coulomb/second or Ampere (A).
Electric current is also a ratio between the voltage and the amount of resistance at the conductor.
Can be formulated
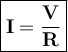
V = Voltage (volts)
R = resistance (ohms)
I=current=4 A
R=resistance=30 Ω
The voltage needed :