Answer:
(a) The probability that the store’s revenues were at least $9,000 is 0.0233.
(b) The revenue of the store on the worst 1% of such days is $7,631.57.
Explanation:
According to the Central Limit Theorem if we have a population with mean μ and standard deviation σ and we take appropriately huge random samples (n ≥ 30) from the population with replacement, then the distribution of the sum of values of X, i.e ∑X, will be approximately normally distributed.
Then, the mean of the distribution of the sum of values of X is given by,
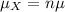
And the standard deviation of the distribution of the sum of values of X is given by,
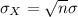
It is provided that:
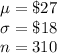
As the sample size is quite large, i.e. n = 310 > 30, the central limit theorem can be applied to approximate the sampling distribution of the store’s revenues for Sundays by a normal distribution.
(a)
Compute the probability that the store’s revenues were at least $9,000 as follows:
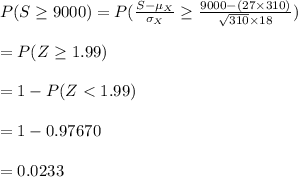
Thus, the probability that the store’s revenues were at least $9,000 is 0.0233.
(b)
Let s denote the revenue of the store on the worst 1% of such days.
Then, P (S < s) = 0.01.
The corresponding z-value is, -2.33.
Compute the value of s as follows:
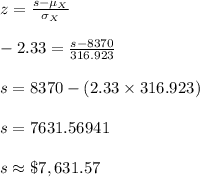
Thus, the revenue of the store on the worst 1% of such days is $7,631.57.