The dissociation constant of the base : 7.4 x 10⁻⁴
Further explanation
Butylamine, C4H9NH2 Is A Weak Base
Kb is the dissociation constant of the base.
LOH (aq) ---> L⁺ (aq) + OH⁻ (aq)
![\rm Kb=([L][OH^-])/([LOH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/t3aug72g7epgpxims4v0c78tk4ldakaqbe.png)
[OH⁻] for weak base can be formulated :
![\tt [OH^-]=√(Kb.M)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/dr61xck9e552tl9vnrfi5y5xqi16i4hg9q.png)
pH of solution : 12
pH+pOH=14, so pOH :
14-12 = 2, then :
![\tt [OH^-]=10^(-pOH)\\\\(OH^-]=10^(-2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gdxss6gbet4q2ocx1hzda4r42dwve47iyl.png)
the the dissociation constant (Kb) =
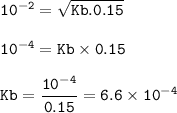
Or you can use from ICE method :
C4H9NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ C4H9NH3+(aq) + OH-(aq)
0.15
x x x
0.15-x x x
![\tt Kb=(x^2)/(0.15-x)\rightarrow x=[OH^-]\\\\Kb=(10^(-4))/(0.15-10^(-2))=7.14* 10^(-4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nsx1t0psynsyzlr70nrszvt6t5osl0ikds.png)