Answer:
The first dissociation occurred at 0.00311 M and the second at 0.0000484 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
The ICE table can be computed as follows:
H2A → HA⁻ + H⁺
Initial 0.10 0 0
Change -x x x
Equilibrium 0.10 - x x x
![Ka_1 = ([HA^-][H^+])/([H_2A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/r5s2t0kfn0oc00i68incabn5oroue377qz.png)
![1.0* 10^(-4)= ([x][x])/([0.10-x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/sknsulc9czvo862oj5xcc1p1xv7r0czd9b.png)
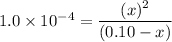
By solving for x;
x² = (1.0 × 10⁻⁴ × 0.1)
x =
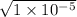
x = [H⁺] =[HA⁻] = 0.00311 M
The acid then further its dissociation again, So;
The ICE table can be computed as follows:
HA⁻ → A⁻ + H⁺
Initial 0.00311 0 0.00311
Change -x x x
Equilibrium 0.00311 - x x 0.00311 + x
![Ka_2 = ([A^-][H^+])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ubrnk9z6ux1j9q52h7izec673h3sm24bb1.png)
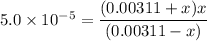
By solving for x;
x = [H⁺] = 0.0000484 M
Therefore, the first dissociation occurred at 0.00311 M and the second at 0.0000484 M.