Answer:
The resultant velocity has a magnitude of 38.95 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Vector Addition
Given two vectors defined as:
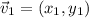
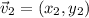
The sum of the vectors is:
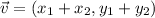
The magnitude of a vector can be calculated by
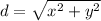
Where x and y are the rectangular components of the vector.
We have a plane flying due west at 34 m/s. Its velocity vector is:
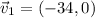
The wind blows at 19 m/s south, thus:
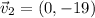
The sum of both velocities gives the resultant velocity:
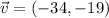
The magnitude of this velocity is:
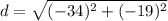
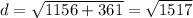
d = 38.95 m/s
The resultant velocity has a magnitude of 38.95 m/s