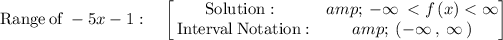Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Finding the domain:
The domain of a function is the set of possible input values for which the function is real and defined.
Given the function
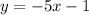
The function has no undefined points nor domain constraints. Hence, the domain is
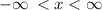
i.e.
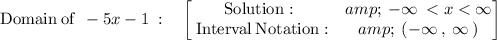
Finding the range:
The range of a function is the set of possible output values (dependent variable y values) for which a function is defined.
The range of polynomials with odd degree is all the real numbers.
Hence, the domain is
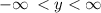
i.e.