Evaluating at infinity, we have:
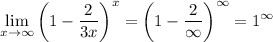
Therefore, we must perform an algebraic manipulation to obtain an expression similar to the definition of e. To do so, we first modify the expression inside the parentheses (and denote the limit as L):
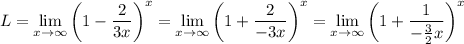
So in the exponent we must have
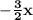 somehow. Note that this is achieved by doing:
somehow. Note that this is achieved by doing:
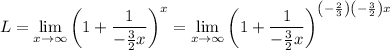
Then we use properties of exponents:
![\displaystyle L = \lim_(x \to \infty){\left( 1 + (1)/(-(3)/(2)x) \right)^{\left(-(2)/(3)\right)\left(-(3)/(2)\right)x} = \left[ \lim_(x \to \infty){\left( 1 + (1)/(-(3)/(2)x) \right)^{-(3)/(2)x} \right]^{-(2)/(3)}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/g77tpkef8zhg5zft9vdk.png)
We can now calculate the limit (noting that what is inside the square brackets is the definition of e with n =
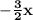 ):
):
![\displaystyle L = \left[ \lim_(x \to \infty){\left( 1 + (1)/(-(3)/(2)x) \right)^{-(3)/(2)x} \right]^{-(2)/(3)} = e^{-(2)/(3)} = (1)/(e^(2/3)) = \frac{1}{\sqrt[3]{e^2}}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/g6zjkpf4ua5kb22coyog.png)