Answer:
b. 1.5 atm.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the undergoing chemical reaction suggests that two moles of A react with one moles of B to produce two moles of C, for the final pressure we can write:
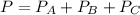
Now, if we introduce the stoichiometry, and the change in the pressure
 we can write:
we can write:
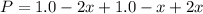
Nevertheless, since the reaction goes to completion, all A is consumed and there is a leftover of B, and that consumed A is:
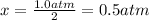
Thus, the final pressure is:
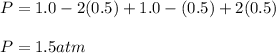
Therefore the answer is b. 1.5 atm.
Best regards!