Answer:
The instantaneous velocity at
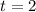 is
is
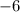 .
.
Explanation:
We have the position as the function
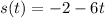
As we know that the velocity is the rate of change of position over time, so it is basically the derivative of the function.
so finding the derivate of
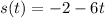
∴
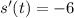
The instantaneous velocity at
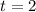
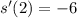
Therefore, the instantaneous velocity at
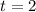 is
is
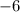 .
.
Please note that the negative value indicates the direction of movement, in this case, it would be backward.