Answer:
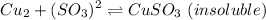
![$Cu_2+2(SO_3)^2 \rightleftharpoons [Cu(SO_3)_2]_2 \ (soluble)$](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mpzpy3k1s0nd624y6nm8vfk28g0gf6gx32.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
A ligand may be defined as a molecule or an ion or that binds to the central metal atom in order to form a more coordination complex. Sulfite is one such ligand and it behaves similarly as hydroxide as a ligand.
Now, according to the question, when we react copper with sulfite ion, it forms copper sulfite. The equation is
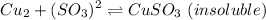
Now when excess of the sulfite ion is used in the reaction, we get a complex formation, which is shown by
![$Cu_2+2(SO_3)^2 \rightleftharpoons [Cu(SO_3)_2]_2 \ (soluble)$](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mpzpy3k1s0nd624y6nm8vfk28g0gf6gx32.png)
The way the sulfite reacts is quite similar to hydroxide ion where they form a complex ion when hydroxide ion in excess is used in the reaction with metal cation.