Answer:
The sum of the two solutions to the given equation is 1/3.
Explanation:
Nature of Roots of a Second-Degree Equation
Given a quadratic equation:
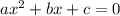
The roots of the equation are:
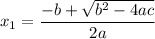
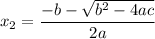
The sum of the roots is:
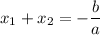
The sum of the roots of a quadratic equation is equal to the negation of the coefficient of the second term, divided by the leading coefficient.
We are given the equation:
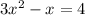
Rearranging:
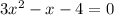
The coefficient b is b=-1, and the leading coefficient is a=3, thus the sum of the roots is:
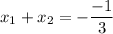
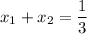
The sum of the two solutions to the given equation is 1/3.