The correct answer is 10 units.
We can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side, which is the hypotenuse of the triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In this case, the other two sides have lengths of 8 units and 6 units . Therefore, we can set up the following equation:
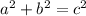
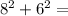
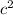
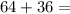
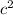
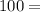
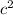
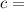
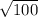

Therefore, the length of the missing side is 10 units.
The question probable maybe:
Find the length of the missing side. The triangle is not drawn to scale. If a=8 and b=6 , what is c?