Hi there!
Recall the equation for magnetic force on a wire:
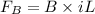
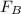 = Magnetic force (N)
= Magnetic force (N)
B = Magnetic field strength (0.2 T)
i = Current in wire (? A)
L = Length of wire (0.25 m)
This is a cross-product, but we can assume the field is perpendicular to the current since it is not explicitly stated otherwise.
The equation for the weight of an object (Force due to gravity) is given by:
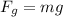
m = mass of object (0.01 kg)
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
Set the two equations equal to each other and solve for 'i'.
 .
.