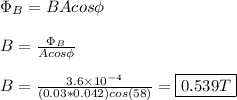Hi there!
Recall the equation for magnetic flux.
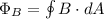
We can also rewrite this as:
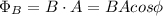
B = Magnetic field strength (T)
A = Area of surface (m²)
φ = angle between the surface's area vector and magnetic field
Since the rectangular surface is horizontal, its perpendicular area vector points straight UP.
The magnetic field makes an angle of 32° with the surface but makes an angle complementary to this angle with the AREA VECTOR. (Think: the vertical)
Complementary of 32° ⇒ 90° - 32° = 58°
Now, we can rearrange the above equation to solve for the magnetic field.