Answer:
The magnitude of the net force is 0.204 N.
Step-by-step explanation:
The net force acting upon the air glider is:
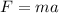
Where:
m: is the mass of the air glider = 1.5 kg
a: is the acceleration
First, we need to find the acceleration. Since we have the initial and final speed we can calculate the acceleration as follows:
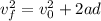
Where:
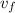 : is the final speed = 1.798 m/s
: is the final speed = 1.798 m/s
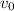 : is the initial speed = 1.872 m/s
: is the initial speed = 1.872 m/s
d: is the distance = 1 m
The acceleration is:
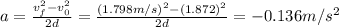
The minus sing is because the air glider is desaccelerating.
Now, the magnitude of the net force is:
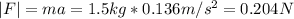
Therefore, the magnitude of the net force is 0.204 N.
I hope it helps you!