Answer: 0.1335
Explanation:
Given: Children's IQs follow a normal distribution with mean
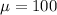 and standard deviation of
and standard deviation of
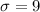 .
.
Let X be the IQ of a random child.
The probability that a randomly selected child has IQ above 110 = P(X>100)
![=P((X-\mu)/(\sigma)>(110-100)/(9))\\\\=P(Z>1.11)\\\\=1-P(Z<1.11)\ \ \ \ [P(Z>z)=1-P(Z<z)]\\\\=1-0.8665\\\\=0.1335\ \ \ [\text{By p-value table}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/xub0nnjcxo8i4zmor67snpwcqhcnch9rf7.png)
Hence, the probability that a randomly selected child has IQ above 110= 0.1335