Answer:
2.925 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us assume g = 9.8 m/s²
There is energy transfer by heat from the system, hence Q is negatitive
Q = -(10 kJ per kg)(5 kg) = -50 kJ
Since the specific internal energy decreases, hence it is negative.
U = - 10 kJ/kg(5 kg) = -50 kJ
Since there is decrease in elevation, hence the change in elevation should be negative.
ΔPE = mgΔh = 5kg × 9.8 m/s² × -75 m = -3675 J = -3.675 kJ
There is increase in velocity, hence change in kinetic energy is positive:
ΔKE =
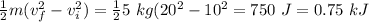
Energy in - Energy out = ΔE
Q - W = ΔKE + ΔPE + ΔU
W = Q - (ΔKE + ΔPE + ΔU)
W = -50 kJ - (0.75 kJ + (-3.675 kJ) + (-50 kJ))
W = -50 kJ - (0.75 kJ - 3.675 kJ - 50 kJ)
W = -50 kJ - (-52. 925 kJ) = -50 kJ + 52. 925 kJ
W = 2.925 kJ