Answer:
Maximum absolute value of f=61/2 at (
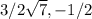 ) and (
) and (
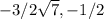 )
)
Minimum absolute value of f=-10 at (0,-5)
Explanation:
We are given that
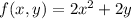
Let
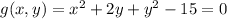
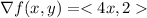
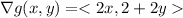
Using Lagrange multipliers
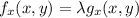
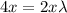
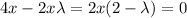
x=0 or
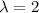
If x=0
Then,
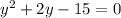
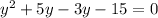
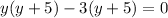
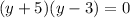
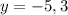
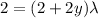
If
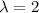
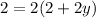
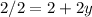
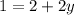
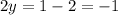
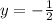
If y=-1/2
Then,
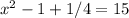
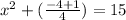
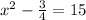
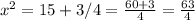
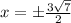
Therefore, possible extreme points are
(0,-5),(0,3),(
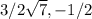 ) and (
) and (
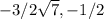 )
)
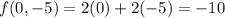
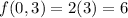
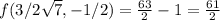
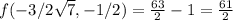
Therefore, maximum absolute value of f=61/2 at (
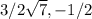 ) and (
) and (
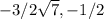 )
)
Minimum absolute value of f=-10 at (0,-5)