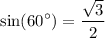Answer:
See Below.
Explanation:
Since ΔABC is an equilateral triangle, this means that ∠A, ∠B, and ∠C all measure 60°.
Furthermore, all sides of the triangle measure 2a.
We know that AD⊥BC. Since this is an equilateral triangle, any altitude will be a perpendicular bisector. Therefore, BD = DC, ∠CAD = 30° and ∠C = 60°.
Additionally, the measures of the segments are: BD = DC = (2a) / 2 = a.
Let’s use the right triangle on the right. Here, we have that DC = a and AC = 2a.
Recall that sine is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. Therefore, sin(C) or sin(60°) will be AD / AC. We can find AD using the Pythagorean Theorem:
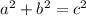
a is DC, b is AD, and c is AC.
Substitute in appropriate values:
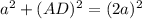
Solve for AD:
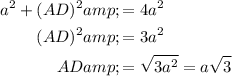
Sine is the ratio of the opposite to the hypotenuse:
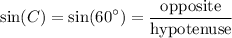
Substitute:
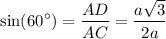
Simplify. Hence, regardless of the value of a: