Answer:
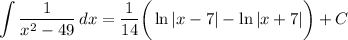
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra I
Terms/Coefficients
Pre-Calculus
- Partial Fraction Decomposition
Calculus
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(x) + g(x)] = (d)/(dx)[f(x)] + (d)/(dx)[g(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/kqosumt4896r7x44jgtw0o7kk6g4d3irvr.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Integration
- Integrals
- [Indefinite Integrals] integration Constant C
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
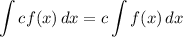
Integration Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \int {[f(x) \pm g(x)]} \, dx = \int {f(x)} \, dx \pm \int {g(x)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ytcjdhza3nvop8ti8icbfc977nz2k5ug6b.png)
U-Substitution
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
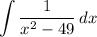
Step 2: Integrate Pt. 1
- [Integrand] Factor:
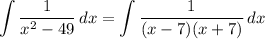
- [Integrand] Split [Partial Fraction Decomp]:
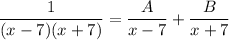
- Rewrite:
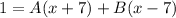
- [Decomp] Substitute in x = 7:
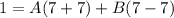
- Simplify:
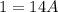
- Solve:
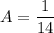
- [Decomp] Substitute in x = -7:
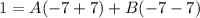
- Simplify:
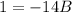
- Solve:
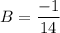
- [Split Integrand] Substitute in variables:
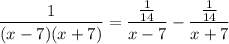
Step 3: Integrate Pt. 2
- [Integral] Rewrite [Split Integrand]:
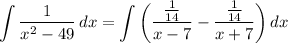
- [Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Addition/Subtraction]:
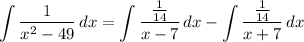
- [Integrals] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
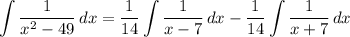
- Factor:
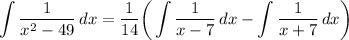
Step 4: Integrate Pt. 3
Identify variables for u-substitution.
Integral 1
- Set u:
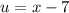
- [u] Differentiate [Basic Power Rule, Derivative Properties]:
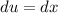
Integral 2
- Set z:
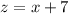
- [z] Differentiate [Basic Power Rule, Derivative Properties]:
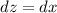
Step 5: Integrate Pt. 4
- [Integrals] U-Substitution:
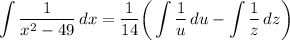
- [Integrals] Logarithmic Integration:
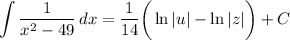
- [Variables] Back-Substitute:
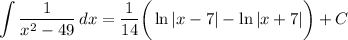
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Integration