The question is incomplete. Here is the complete question.
Calcium oxide,
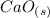 , has been proposed as a substance that can be used to heat water quickly for portable heating packs or for cooking. When placed in water,
, has been proposed as a substance that can be used to heat water quickly for portable heating packs or for cooking. When placed in water,
 reacts as shown by hte equation below:
reacts as shown by hte equation below:
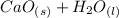 ⇄
⇄
a) A student wants to design a heating pad that could heat a 150.0 g sample of water from 25.0°C to 60.0°C.
(i) Calculate the amount of heat, in joules, that the water must absorb for its temperature to change by this amount. (Assume that specific heat capacity of water is 4.18J/(g.°C).)
(ii) Calculate the minimum mass of
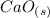 that the student would need to use in order to cause this temperature change.
that the student would need to use in order to cause this temperature change.
Answer: (i) Q = 21,945J
(ii) m = 467.87g
Step-by-step explanation: Energy necessary for the water to absorb to heat up is calculated by:
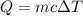
Q is heat
c is specific heat capacity, in this case in J/g.°C
 is change in temperature
is change in temperature
(i) Calculating amount of heat:
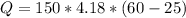
Q = 21945J
The water needs 21,945 joules to increase by that amount of temperature.
(ii) According to the chemical equation:
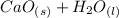 ⇄
⇄
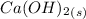
it is needed 1 mol of each reagent to produce 1 mol of product.
Molar mass of water is 18g/mol. For 150g, there are:
n =
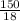
n = 8.34 mols
Molar mass of CaO is 56.1g/mol. For 8.34 mols:
m = 8.34*56.1
m = 467.87g
For calcium oxide to increase temperature in 35°C, the minimum necessary is 467.87 grams.