Answer:
The decision rule is
Fail to reject the null hypothesis
The conclusion is
There is no sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean CPA of all students who vote is lower than the CPA of students who do not vote
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The first sample size is

The sample mean is
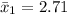
The standard deviation is
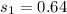
The second sample size is
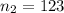
The sample mean is
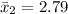
The level of significance is
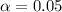
The standard deviation is
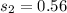
The null hypothesis is
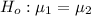
The alternative hypothesis is
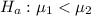
Generally the test hypothesis is mathematically represented as
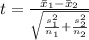
=>
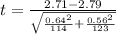
=>
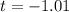
Generally given that variance are not equal (the standard deviation squared of both population are not equal ) the degree of freedom is mathematically represented as
![df = ([(s_1^2)/(n_1 ) + (s_2^2)/(n_2) ])/(([(s_1^2)/(n_1)]^2 )/(n_1 - 1) + ([(s_2^2)/(n_2)]^2 )/(n_2 - 1))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/b7vam73izilvshs5v96gsslunf2qqkibno.png)
=>
![df = ([(0.64^2)/(114) + (0.56^2)/(123) ])/(([(0.64^2)/(114)]^2 )/(114 - 1) + ([(0.56^2)/(123)]^2 )/(123 - 1))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/f14fkwbfluf01ztbzgzacvam7l6h54wokx.png)
=>
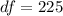
Generally from the t distribution table the the probability of (t < -1.01) at a degree of freedom of
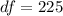 is
is
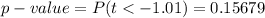
Generally the value obtained we see that
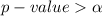 so
so
The decision rule is
Fail to reject the null hypothesis
The conclusion is
There is no sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean CPA of all students who vote is lower than the CPA of students who do not vote