Answer:
The average velocity and average speed of the dog are 2.262 meters per second and 6.787 meters per second, respectively.
Step-by-step explanation:
From Physics we must remember the definitions of average speed and average velocity, both measured in meters per second. Velocity is a vectorial quantity, that is, it has both magnitude and direction, whereas speed is an scalar quantity, which is a quantity that is represented solely by its magnitude. We assume that dog moves at constant speed.
For the case of the dog, we get that average speed and average velocity of the animal are, respectively:
Average velocity:
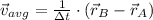 (Eq. 1)
(Eq. 1)
Where:
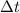 - Travelling time of the dog, measured in seconds.
- Travelling time of the dog, measured in seconds.
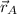 - Initial vector position of the dog, measured in meters.
- Initial vector position of the dog, measured in meters.
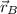 - Final vector position of the dog, measured in meters.
- Final vector position of the dog, measured in meters.
Average speed:
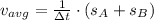 (Eq. 2)
(Eq. 2)
Where
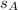 and
and
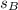 are the travelled distances of each stage, measured in meters.
are the travelled distances of each stage, measured in meters.
If we know that
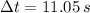 ,
,
![\vec r_(A) = 0\,\hat{i}\,\,\,[m]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/kjn5d6lpzlt7o32pllwkf70bfx8ifm72m6.png) and
and
![\vec r_(B) = 25\,\hat{i}\,\,\,[m]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/q6v16li84i5ir430569olwdnysk5bav9ql.png) ,
,
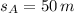 and
and
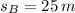 , average velocity and average speed are, respectively:
, average velocity and average speed are, respectively:
![\vec v_(avg) = (1)/(11.05\,s)\cdot (25\,\hat{i})\,\,\,[m]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ukk9l1243q7t227rqcf7vp6yij81948w8o.png)
![\vec v_(avg) = 2.262\,\hat{i}\,\,\,\left[(m)/(s) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/92t1jt08rkf66r6lh7rio0rmaz44cxy9is.png)
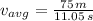
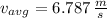
The average velocity and average speed of the dog are 2.262 meters per second and 6.787 meters per second, respectively.