Answer:
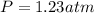
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, since the total pressure in the container includes the pressures of both hydrogen and water:
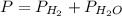
For the reacting solution of HCl, based on the 6:3 mole ratio with hydrogen in the chemical reaction, we can next compute the yielded moles o hydrogen:
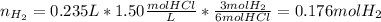
Then, by using the ideal gas equation we compute the pressure of hydrogen for the collected 3.60 L at 25.0 °C (298.15 K):
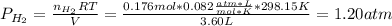
Finally, since the vapor pressure of water in at is 0.03129, the total pressure is then:
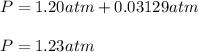
Best regards!