Answer:
The ratio of the magnitude of the electric force on the bee to the magnitude of the bee's weight is 2.35 x 10⁻⁶
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
mass of the honeybee, m = 0.1 g
charge acquired by the honeybee, Q = 23pC = 23 x 10⁻¹² C
the electric field near the earth's surface, E = 100 N/C
The magnitude of the electric force on the bee is given by;
F = QE
F = (23 x 10⁻¹²)(100) = 23 x 10⁻¹⁰ N
The weight of the bee is given by;
W = mg
W = 0.1 x 10⁻³ x 9.8
W = 9.8 x 10⁻⁴ N
The the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force on the bee to the magnitude of the bee's weight is given by;
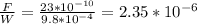
Therefore, the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force on the bee to the magnitude of the bee's weight is 2.35 x 10⁻⁶