Answer: a) A decrease in the solubility of an ionic compound as a result of the addition of a common ion : Common ion effect
b) The mass of a salt in grams that will dissolve in 100 mL of water: Solubility
c) A solution that has dissolved the maximum amount of a compound at a given temperature. Any further addition of salt will remain undissolved: Saturated solution
d) The product of the molarities of the dissolved ions, raised to a power equal to the ion's coefficient in the balanced chemical equation : Solubility product constant
e) The maximum number of moles of a salt that will dissolve in 1 L of solution : Molar solubility
Step-by-step explanation:
Solubility is expressed usually as the mass of solute per 100 grams or 100 ml of solvent.
Molar solubility of a solid is expressed as the concentration of the dissolved solid in a saturated solution.
Solubility product constant is defined as the equilibrium constant in which a solid ionic compound is dissolved to produce its ions in solution. It is represented as
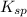
The common-ion effect is the decrease in solubility of a sparingly soluble salt by the addition to the solution of a soluble compound with an ion in common with the precipitate.
Saturated solution is defined as the solution in which no more solute particles can be dissolved in the solvent.