Answer:
C ≈ 1.44 × 10⁻³ mol/m³
Step-by-step explanation:
The given information are;
The liquid volume the pond can hold = 104 m³
The volume of inflow into the pond = 5 m³/h
The volume of outflow into the pond = 5 m³/h
The concentration of the chemical in the inflow water = 0.01 mol/m³
The concentration of the chemical discharged directly into the water = 0.1 mol/h
The concentration,
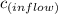 , of chemical that enters the water through inflow per hour is given as follows;
, of chemical that enters the water through inflow per hour is given as follows;
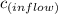 = 0.01 mol/m³ × 5 m³/h = 0.05 mol/h
= 0.01 mol/m³ × 5 m³/h = 0.05 mol/h
The concentration,
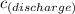 , of chemical that enters the water through direct discharge per hour is given as follows;
, of chemical that enters the water through direct discharge per hour is given as follows;
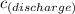 = 0.1 mol/h
= 0.1 mol/h
The total concentration that enters the pond per hour is given as follows;
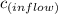 +
+
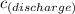 = 0.1 mol/h + 0.05 mol/h = 0.15 mol/h
= 0.1 mol/h + 0.05 mol/h = 0.15 mol/h
Whereby the water in the pond properly mixes with the pond, we have;
The concentration of chemicals (C) in the outflow water = 0.15 mol/(104 m³) ≈ 0.00144 mol/m³
C ≈ 1.44 × 10⁻³ mol/m³.