Answer:
a. First order.
b.
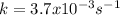
c.
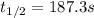
d.
![[A]=0.111M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/23xizsqi8nf12a166btcztktqhxg4leriu.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
a. In this case since the slope is in s⁻¹ we can infer that the lineal form of the rate law is:
![ln[A]=-kt+ln[A]_0](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zl6hkxls32fdbig5n54ufm0eszwmx4iuir.png)
Which is also:
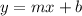
It means that the reaction is first-order as slope equals the negative of the rate constant which also has units of first-oder reaction.
b. Since the slope is −3.7 x 10−3 s−1 the rate constant is:
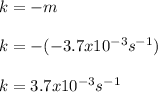
c. For first-order reactions, the half-life is:
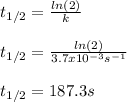
d. In this case, since the integrated first-order rate law is:
![[A]=[A]_0exp(-kt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zoyge5j1cfskjd65o8eidus7s0pcuhr357.png)
The concentration once 220 seconds have passed is:
![[A]=0.250Mexp(-3.7x10^(-3)s^(-1)*220s)\\\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tf9hkys7ske4i6m89k6sf605vk52weg8yp.png)
![[A]=0.111M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/23xizsqi8nf12a166btcztktqhxg4leriu.png)
Regards.