Answer:
A.
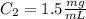
B.
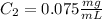
C.
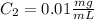
D.
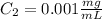
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, we must compute the final concentration in all the cases so we solve for it in the given equation:
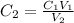
Thus, we proceed as follows:
A. Here, the final diluted solution includes the 300 μL of the 5 mg/ml-BSA and the 700 μL of TBS.
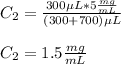
B. Here, the final diluted solution includes the 50 μL of the 1.5 mg/ml-BSA, the 450 μL of water and the 500 μL of TBS.
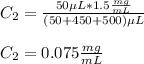
C. Here, the final diluted solution includes the 10 μL of the 1 mg/ml-BSA and the 990 μL of TBS.
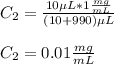
D. Here, the final diluted solution includes the 10 μL of the 0.1 mg/ml-BSA and the 990 μL of TBS.
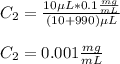
Best regards.