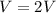Answer:
The value is
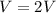
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The length of the wire is
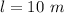
The current density is
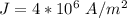
The conductivity is
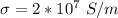
Generally conductivity is mathematically represented as
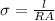
Here R is the resistance which is mathematically represented as
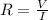
Here I is the current which is mathematically represented as
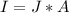
So
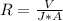
And
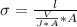
=>
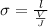
=>
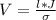
=>
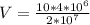
=>