Answer:
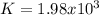
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the reaction:
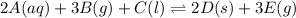
We notice it is undergone as heterogeneous equilibrium, that is why, for the thermodynamic equilibrium constant we consider the aqueous species only, that is the concentration of A to the second power (stoichiometric coefficient) only:
![K=(1)/([A]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6d1ibshtfze44et2jkiasm8ripjsrf0zj2.png)
Thus, the equilibrium constant turns out:
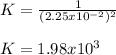
Clearly, B, C, D and E are not considered as they are gaseous, liquid, solid and gaseous respectively, and based on the procedure to write the law of mass action, they are not considered due to different phases.
Best regards.