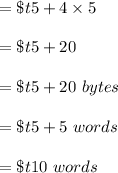Answer:
Follows are the solution to this question:
Step-by-step explanation:
In point a:
Let,
The address of 1-bit memory to add in 2 location:
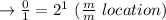
The address of 2-bit memory to add in 4 location:
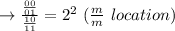
similarly,
Complete 'n'-bit memory address' location number is =
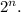 Here, 12-bit memory address, i.e. n = 12, hence the numeral. of the addressable locations of the memory:
Here, 12-bit memory address, i.e. n = 12, hence the numeral. of the addressable locations of the memory:
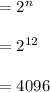
In point b:
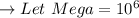
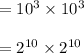
So,
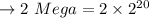
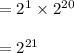
The memory position for '
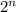 ' could be 'n' m bits'
' could be 'n' m bits'
It can use
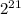 bits to address the memory location of 21.
bits to address the memory location of 21.
That is to say, the 2-mega-location memory needs '21' bits.
Memory Length = 21 bit Address
In point c:
 element array addresses are given by:
element array addresses are given by:
![\to address [i] = B+w * (i-LB)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/csi1qaxg1f9djg3lbcm032uet0j915o5sd.png)

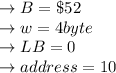
![\to address [10] = \$ 52 + 4 * (10-0)\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/b67aindv86kj3r8ojapdcqv4wjh6kqcjzw.png)
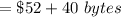
1 term is 4 bytes in 'MIPS,' that is:
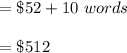
In point d:
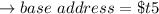
When MIPS is 1 word which equals to 32 bit :
In Unicode, its value is = 2 byte
In ASCII code its value is = 1 byte
both sizes are < 4 byte
Calculating address:
![\to address [5] = \$ t5 + 4 * (5-0)\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/computers-and-technology/college/dycd7e8hc23d71lpgs2dgzxajwuenctibz.png)