Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
a )
focal length of mirror = 20 cm
a ) radius of curvature = 2 x focal length = 2 x 20 = 40 cm
b )
c ) object distance u = 15 cm
image distance v = ?
focal length f = 20 cm from the formula
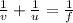
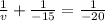
v = + 60 cm
So image is magnified . It will be formed on the other side of the mirror .It will be virtual .
d )
The image is magnified when object is placed between 2 f and f or between centre of curvature and focal length . In this case image is real and magnified . The image is magnified when object is placed between focal length and the pole . In this case image is virtual .