Answer:
The amount of heat is 431.12 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Mass of Ba = 1.50 g
Mass of water = 100.0 g
Initial temperature = 22.00°C
Final temperature = 33.10°C
The reaction is,
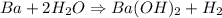
We need to calculate the heat
Using formula of heat
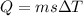
Where, m = mass
s = specific heat
 temperature
temperature
Put the value into the formula
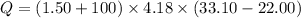
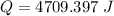
We need to calculate the amount of heat per mole
Using formula of energy per mole
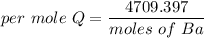
Put the value into the formula
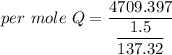
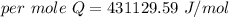
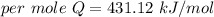
Hence, The amount of heat is 431.12 kJ/mol.