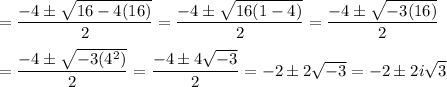Answer:
-3 comes from combining 1 and -4
Explanation:
The -3 under the radical is the result of combining the terms
16 -4(16) = 16(1 -4) = 16(-3) = -3(16)
16 is factored out. It is done this way because 16 is a perfect square factor, so wants to maintain that identity while you figure out the rest of the radical.