Answer:
C. Nernst equation
Step-by-step explanation:
The Nernst Equation is used to find the equilibrium potential of an ion.
It tells you only what the equilibrium potential for an individual ion is, not what the summed effect of all ions is on the membrane potential.
The formula for Nernst Equation is:
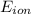 =
=
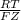 In
In
![([ion]_(out) )/([ion]_(in) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/6y1a4dzuryacrv77mkhvexu817d271bawn.png)
where F is Faraday Constant, R = gas constant, 8.314 J/mol K
, T = temperature, in K, Z stoichiometric number of electrons in the reaction, is the Reduction Potential in V.
Kindly note that, if we have a squid giant axon at rest with normal intracellular and extracellular ion concentrations. If the membrane permeability to K+ ions is increased, the K+ equilibrium potential (Nernst potential) will stay the same.